Database¶
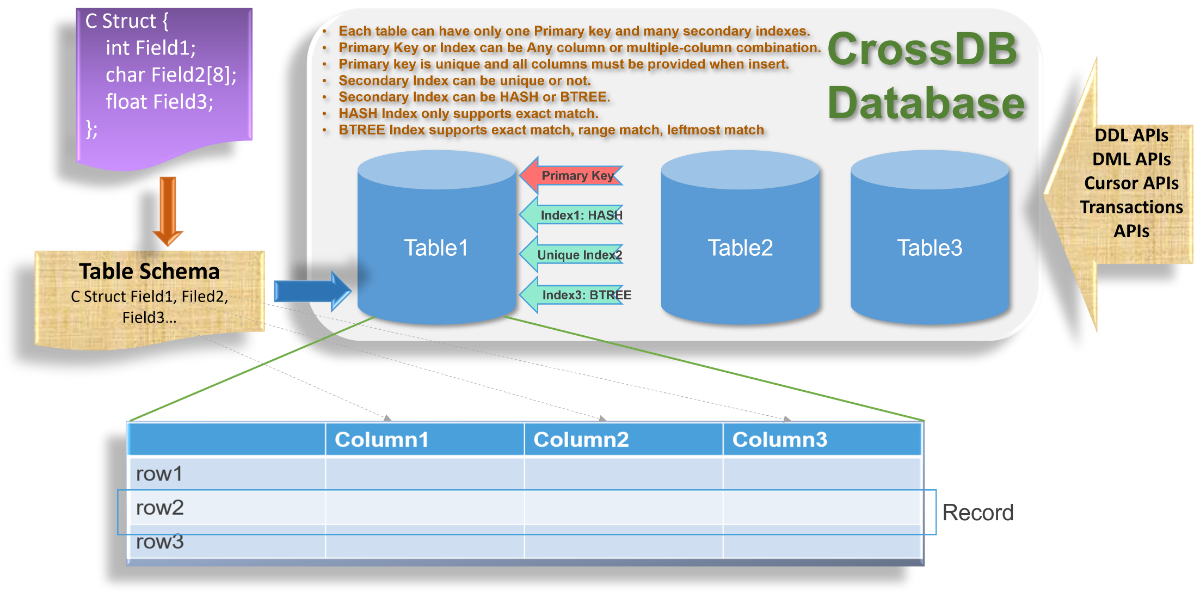
CrosDB Database is a collection of tables.
Steps to define a database
- Decide where to store the database: on disk, on ramdisk or in memory.
- Decide the database is accessed by single process or multiple proceses.
- Use cross_dbCreate to create or open database.
- Use Schema to define table scheam.
- Decide Table Primary Key: fields list, index type.
- Use cross_dbTblCreate to create or open table with schema defined above and provide the primary key.
- Decide how many secondary indexes: fields list, index type, whether unique.
- Use cross_dbIdxCreate to create table secondary index.
Storage Mode¶
On-Disk Database
- Database is on persistent disk, survive with power cycle.
- If you have data persistency requirements, please use this type. The performance is ver high.
- You need use transaction to guarantee data integrity even power cycle happened.
RamDisk Database
- Database is on
ramdisktmpfsramfs(CROSS_RAMDISK), survive with process restart, lose after power cycle. - This is designed for process runtime databse and the transaction performance is higher than On-Disk database.
- The performance is almost the same with In-Memory database.
- For Linux embedded system, this is the prefered database as the database can be viewed and stayed there even process crashed.
In-Memory Database
- Database is in memory(
CROSS_INMEM), survie when process is runnig, lose after process terminates. - This is not recommented, but if you don't want the process runtime database visible, it's the solution.
Access Mode¶
Exclusive
- Database is accessed exclusively by single process with best performance.
Shared
- Databse is accessd by multiple process(
CROSS_SHARED), then performance will be low as file lock is used to access DB which can recover lock when process crashed.
Note
Database is accessed exclusively by default.
Guide¶
- Database is stored on disk by default.
- If path(absoulte or relative) is not provided, DB is stored in current folder.